Why Gas Network Outshines Chainlink and Pyth in Gas Optimization
By Will McKinnon Updated August 29, 2025

Summary
- Blockchains generated over $6.8 billion in transaction fees during 2024 but gas pricing remains inefficient and mostly handled offchain.
- Gas Network introduces a specialized oracle that brings gas pricing onchain enabling real-time predictions and optimization across more than 35 chains.
- By focusing on eliminating systematic overpayments and failures Gas Network positions itself to capture significant value in the rapidly growing cross-chain market.
Introduction
Blockchains generated over $6.8B in transaction fees during 2024, with Ethereum alone accounting for about $2.5B annually. Yet despite this massive market, transaction pricing remains a largely offchain process that is both underoptimized and opaque. Gas Network, developed by the veteran team at Blocknative, addresses this fundamental inefficiency by creating the first decentralized oracle network specifically designed to bring gas pricing onchain.
With monthly cross-chain transaction volume consistently ranging between $1.5 billion and $3.2 billion throughout 2024, Gas Network positions itself to capture value in a market where extreme volatility and poor estimation continue to waste hundreds of millions in user funds.
The Multi-Billion Dollar Problem
The scale of gas fee waste is staggering. May 1, 2022 recorded the highest average daily gas cost of $196.63 just to send a transaction, while individual events have proven even more costly. During the Bored Ape Yacht Club “Otherside” land sale in 2022, one user spent $44,000 in gas fees to mint just two NFTs, with reports of users paying up to $7,000 in gas fees per transaction. At the end of the mint, investors had spent over $180 million in gas fees alone.
Even more recently, gas fees pushed beyond 170 gwei in March 2024, with the average charge to complete a typical NFT transaction eclipsing $370. This extreme volatility persists still because users pay gas fees for failed transactions, as validators must verify and attempt to execute transactions regardless of success.
Cross-chain operations compound the problem as cross-chain swaps require gas fees on both origin and destination networks. Bridge protocols have generated over $100 million in cumulative fees since mid-2020, with unpredictable fee structures that typically range from 1% to 5% of transaction amounts depending on liquidity and activity.
Gas Network’s Solution
Gas Network makes smart contracts gas aware, enabling onchain actors to natively estimate, predict, and optimize gas fees. The system operates through a dedicated “app chain” that aggregates real-time gas predictions for multiple networks, using signed price estimates and blockchain signatures to guarantee message consistency as data moves across chains.
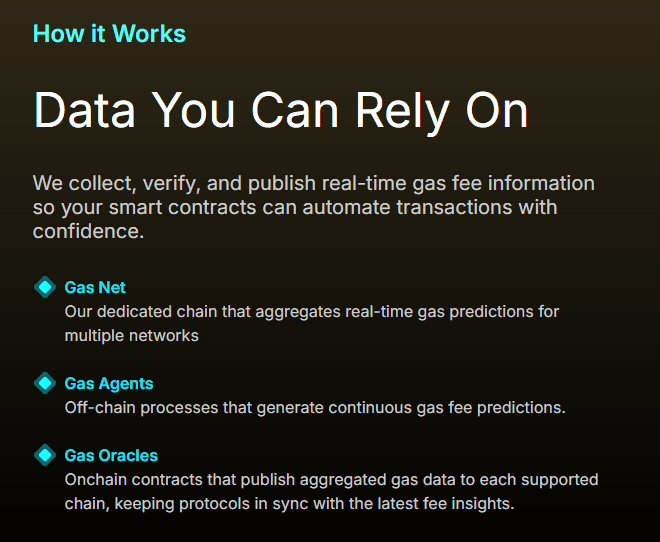
Currently supporting over 35 chains, including Ethereum mainnet and several of its Layer 2’s, Gas Network enables automated decision-making for transaction timing and cost optimization. This directly addresses the inefficiencies that led to the $180 million wasted during the Otherside mint.
Competitive Landscape
Chainlink accounts for a shocking 62% of the $19B oracle sector, leveraging their extensive partnerships with financial titans like J.P. Morgan and Mastercard, as well as leading DeFi protocols like Aave and GMX. However, Chainlink’s general-purpose approach contrasts sharply with Gas Network’s specialization in solving the specific, expensive problem of gas price optimization.
Pyth Network also provides financial market data to smart contracts, specializing in low-latency, high-frequency price data with sub-second updates sourced directly from exchanges and financial institutions. While both Chainlink and Pyth focus on financial data feeds, Pyth’s first-party approach and specialization in high-frequency financial markets make it a closer competitor to Gas Network’s specialized approach. However, neither addresses the unique volatility characteristics of gas pricing that can swing from less than a penny to hundreds of dollars within hours, creating systemating overpayments and failed transaction waste.
Market Positioning
Gas Network’s competitive advantage lies in addressing documented, quantifiable waste within the $6.8 billion annual transaction fee market. While established oracles provide financial data feeds, Gas Network’s specialization enables deeper optimization for the specific challenges of gas pricing, preventing $44,000 individual overpayments and systematic failures that waste millions.
The project’s cross-chain native design and real-time optimziation capabilities directly target inefficiencies that competitors have not adequately addressed, positioning it to capture value form the growing cross-chain acitivity generating $1.5-3.2 billion in monthly volume.
Opportunity and Strategic Outlook
Gas Network faces the challenge of competing against Chainlink’s market dominance and established ecosystem. However, the documented scale of gas fee waste, most notably the examples mentioned above, validates the urgent need for specialized solutions.
Future developments include API access, expansion beyond EVM chains, and enhanced analytics including historical trends, volatility, metrics, and predictive analytics. The project’s specialized focus on a multi-billion dollar inefficiency that general-purpose oracles have not solved represents significant market opportunity. As cross-chain activity expands and gas fee volatility persists, Gas Network’s targeted approach to optimizing blockchain’s largest operational expense positions it to capture significant value.
Conclusion
Gas Network addresses a multi-billion dollar market inefficiency through specialized gas pricing oracles, competing against general-purpose solutions by preventing documented waste that has cost users hundreds of millions in overpaid and failed transaction fees. While established players like Chainlink dominate the broader oracle market, the persistent and expensive nature of gas pricing failures create a clear opportunity for specialized solutions.
With cross-chain activity continuing to grow and gas fee volatility remaining a fundamental challenge in crypto, Gas Network’s targeted approach to this specific but costly problem positions it to capture meaningful market share in an underserved yet critical niche of the blockchain infrastructure ecosystem.
Go, check out their Gas Extension for real-time alerts today! And, don’t forget to follow GasNetwork on X for all the latest updates.
Disclaimer: Beluga has a marketing partnership with Blocknative.
Join the Beluga Brief
Dive deep into weekly insights, analysis, and strategies tailored to you, empowering you to navigate the volatile crypto markets with confidence.
Never be the last to know
and follow us on X